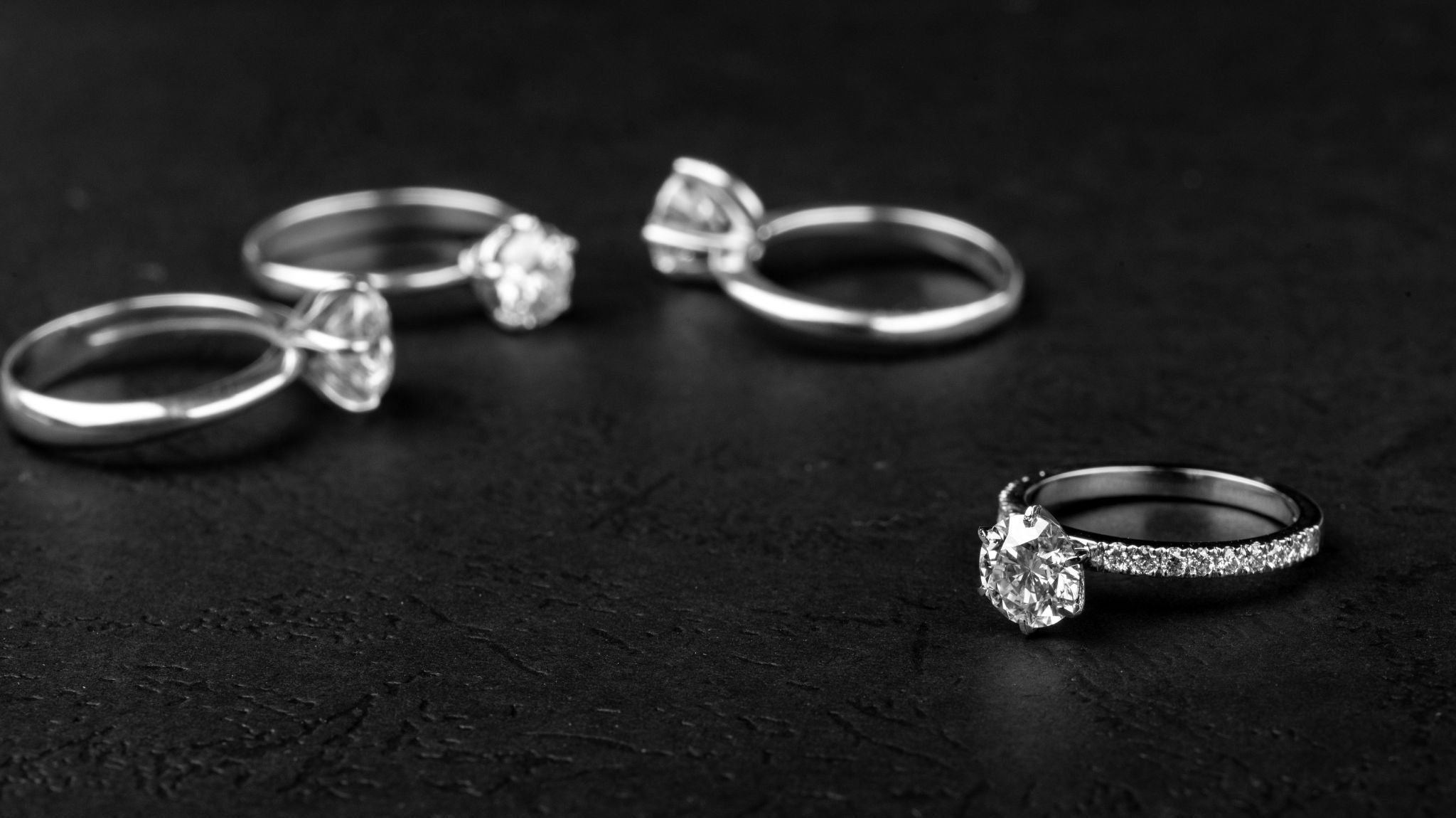
Cut
The cut of a diamond determines the overall appearance of the diamond. A diamond's cut grade is an objective measure of a diamond's light performance, or, what we normally think of as sparkle. When a diamond is cut with the proper proportions, light is returned out of the top of the diamond, giving lots of brilliance and sparkle to the diamond. If it is cut too shallow, light will leak out the bottom; too deep and it escapes out the side of the diamond. There are 5 cut grades that determine how much light reflection and performance the diamond has: Ideal Cut, Very Good Cut, Good Cut, Fair Cut, and Poor Cut.
Color
The color grade refers to the lack of color the diamond has, grading on the whiteness. Every letter from D to Z represents a shade of color. A color grade of D is the highest possible, while Z is the lowest. D is considered very rare and absolutely colorless. Grades F-E are colorless, showing minute traces of color that only an expert gemologist can detect. H-G grades are nearly colorless, as color is difficult to see unless compared side by side to diamonds of a better grade. J-I grades are also colorless, however there is a slight warmth to the stones. M-K grades have faint color, N-R have very light color, and S-Z have light color to the diamonds.
Clarity
Clarity is a way of measuring the number and size of the tiny imperfections that occur in almost every diamond. The clarity usually has the least impact on a diamond's appearance since the imperfections tend to be microscopic, and do not affect the diamond's beauty. Here is a breakdown of the clarity grades: FL- Flawless- No internal or external imperfections. IF-Internally Flawless- No external imperfections. VVS1/VVS2- Very Very Slightly Included- Very difficult to see imperfections, even under 10x magnification. VS1/VS2- Very Slightly Included- Imperfections are not typically seen to the unaided eye. SI1/SI2- Slightly Included- Imperfections may be seen to the unaided eye, and are visible under magnification. I1/I2/I3- Included- Inclusions are eye visible, and are quite noticeable under 10x magnification.
Carat
A diamond carat weight is the measurement of how much a diamond weighs. A metric "carat" is defined at 200 milligrams. Each carat can be subdivided into 100 'points' to allow precise measurements to the 100th decimal place. Any diamond below one carat is sometimes referred to by its 'points' alone. For example: A diamond that weighs 0.25 carats can be called a twenty-five pointer. Diamond weights greater than one carat are expressed in carats and decimals. A 1.06 carat stone would be described as 'one point oh six carats' . Diamond price increases with diamond carat weight since larger diamonds are more rare and therefore more desirable. Yet two diamonds of an equal carat weight may have very different values (and prices) depending on the other 3 C's- Clarity, Color and Cut. All 4 C's go into account for the value of the diamond.